IBM Cloud
IBM Cloud was designed to support a full range of applications: from modern, cloud-native apps and microservices to legacy, monolithic software and systems. It provides companies with the infrastructure needed to build new applications from scratch, modernize existing applications, or both. IBM Cloud is ready to support enterprises at any stage of their journey to cloud.
Video: Welcome to the IBM Cloud
Take a tour of the IBM Cloud console to learn how you can easily start building right away. Get your account set up, create resources from the IBM Cloud catalog, then manage them from your resource list. Visit the Support page to get help with any issues you might run into. The IBM Cloud documentation is also a helpful resource for walking you through common tasks.
Cloud computing, sometimes referred to simply as “cloud,” is the use of computing resources — servers, database management, data storage, networking, software applications, and special capabilities such as blockchain and artificial intelligence (AI) — over the internet, as opposed to owning and operating those resources yourself, on premises.
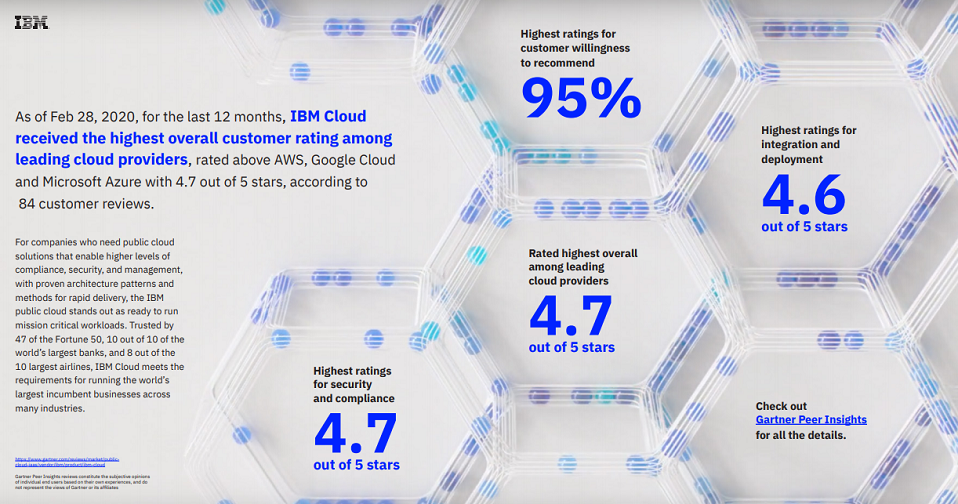
Click here to learn more about IBM’S cloud offerings.
Compared to traditional IT, cloud computing offers organizations a host of benefits:
- Greater cost efficiency. While traditional IT requires you to purchase computing capacity in anticipation of growth or surges in traffic — capacity that sits unused until you grow or traffic surges — cloud computing enables you to pay for only the capacity you need, when you need it. Cloud also eliminates the ongoing expense of purchasing, housing, maintaining and managing infrastructure on premises.
- Improved agility; faster time to market. On the cloud you can provision and deploy (“spin up”) a server in minutes; purchasing and deploying the same server on premises might take weeks or months.
- Greater scalability and elasticity. The cloud lets you scale workloads automatically — up or down — in response to business growth or surges in traffic. And working with a cloud provider that has data centers spread around the world enables you to scale up or down globally on demand, without sacrificing performance.
- Improved reliability and business continuity. Because most cloud providers have redundancy built into their global networks, data backup and disaster recovery are typically much easier and less expensive to implement effectively in the cloud than on premises. Providers who offer packaged disaster recovery solutions— referred to disaster recovery as a service, or DRaaS — make the process even easier, more affordable and less disruptive.
- Continually improving performance. The leading cloud service providers regularly update their infrastructure with the latest, highest-performing computing, storage and networking hardware.
- Better security, built in. Traditionally, security concerns have been the leading obstacle for organizations considering cloud adoption. But in response to demand, the security offered by cloud service providers is steadily outstripping on-premises solutions. According to security software provider McAfee, today 52% of companies experience better security in the cloud than on premises. Gartner has predicted that by this year (2020), infrastructure as a service (IaaS) cloud workloads will experience 60% fewer security incidents than those in traditional data centers.
IBM Cloud Deployment Models
- Public cloud
- Private cloud
- Hybrid cloud
Public Cloud

IBM Public Cloud
IBM public cloud offers a broad range of compute choices, from bare metal and virtual servers, to serverless architectures, to Cloud Foundry apps, to Kubernetes containers.

Advantages
- Ease of Use. With on-demand deployment of a managed Red Hat OpenShift environment and our commitment to the Red Hat ecosystem, it’s easy to connect and migrate.
- Industry-leading compliance. Includes FIPS 140-2 Level 4 HSM cryptocards, for data encryption to meet even the most stringent requirements
- Threat monitoring. Manage threats across all clouds from a centralized security dashboard with IBM Security integration
- Hardened Kubernetes service. Continuous container security, built-in isolation, and network segmentation for application protection
For a closer look at IBM public cloud, see the following video:
Private Cloud
Many companies choose private cloud over Public Cloud (cloud computing services delivered over infrastructure shared by multiple customers) because private cloud is the only way to meet regulatory compliance requirements. Others choose private cloud because their workloads deal with confidential documents, intellectual property, personally identifiable information (PII), medical records, financial data, or other sensitive data.
Private Cloud and IBM Cloud
Advantages
- Full control over hardware and software choices. Private cloud customers are free to purchase the hardware and software they prefer, versus the hardware and software the cloud provider offers.
- Freedom to customize hardware and software. Customers can customize servers in any way they want and software as needed with add-ons or through custom development.
- Greater visibility into security and access control. All workloads run behind the customers’ own firewall.
- Fully enforced compliance with regulatory standards. Companies are not forced to rely on the industry and regulatory compliance offered by the cloud service provider.


Disadvantages
- Higher cost. This can include the cost of purchasing and installing new hardware and software and the cost of managing it, which may involve hiring additional IT staff.
- Limited flexibility. Once an organization invests in hardware and software for its private cloud, adding capacity or new capabilities requires additional purchases.
Hybrid Cloud
IBM Hybrid Cloud
Advantages
- Security and compliance. Hybrid cloud lets organizations deploy highly regulated or otherwise sensitive workloads in private cloud, while still being able to deploy less-sensitive workloads to public cloud services.
- Scalability and resilience. You can’t always predict when workload traffic will spike, and even when you can predict spikes, you can’t always afford to purchase additional private cloud capacity for those spikes only. Hybrid cloud lets you scale up quickly, inexpensively, and even automatically using public cloud infrastructure and then scale back down when the surge subsides—all without impacting the other workloads running on your private cloud.
- Resource optimization and cost savings. Hybrid cloud gives IT more options and flexibility for deploying workloads in a way that makes the best use of on-premises investments and overall infrastructure budget. Deployments can be changed in response to fluctuating workloads or new opportunities.

IBM Cloud Paks
IBM Cloud™ Paks are enterprise-ready, containerized software solutions that give clients an open, faster and more secure way to move core business applications to any cloud. Each IBM Cloud Pak™ includes containerized IBM middleware and common software services for development and management, on top of a common integration layer — designed to reduce development time by up to 84 percent and operational expenses by up to 75 percent.* IBM Cloud Paks run wherever Red Hat® OpenShift® runs and are optimized for productivity and performance on Red Hat OpenShift on IBM Cloud.
To read more about the six IBM Cloud Paks and benifits of each, click here:
IBM Cloud Catalog
The IBM Cloud Catalog lists over 170 services across categories, including:
- Compute – Offers various compute resources, including bare-metal servers, virtual servers, and serverless computing and containers on which enterprises can host their workloads.
- Network – Provides cloud networking services, such as a load balancer, a content delivery network (CDN), virtual private network (VPN) tunnels and firewalls.
- Storage – Offers object, block and file storage for cloud data.
- Management – Provides tools to manage and monitor cloud deployments, such as those for log analysis, automation and Infrastructure as Code (IaC).
- Security – Includes services for activity tracking, identity and access management and authentication.
- Data management – Provides SQL and NoSQL databases, as well as data querying and migration tools.
- Analytics – Offers data science tools such as Apache Spark, Apache Hadoop and IBM Watson Machine Learning, as well as analytics services for streaming data.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) – Uses IBM Watson to deliver services such as machine learning, natural language processing and visual recognition.
- Internet of things (IoT) – Includes the IBM IoT Platform, which provides services that connect and manage IoT devices, and analyzes the data they produce.
- Mobile – Enables a development team to build and monitor mobile applications and their back-end components.
- Developer tools – Includes a command-line interface (CLI), as well as a set of tools for continuous delivery, continuous release and application pipelines.
- Blockchain – Provides IBM’s Blockchain Platform, a software-as-a-service offering to develop apps, enforce governance and monitor Blockchain networks.
- Integration – Offers services to integrate cloud and on-premises systems, or various applications, such as API Connect, App Connect and IBM Secure Gateway.
- Migration – Provides tools to migrate apps to the cloud, such as IBM Lift CLI and Cloud Mass Data Migration.
- VMware – Enables the migration of VMware workloads into the cloud.
The Future of Cloud
To review the eBook, “Achieve Cloud without Compromise”, click here:

